It’s thrilling to envision ourselves being able to finance our dream house, giving our kids the best education possible, and retiring comfortably. But realizing these goals takes more than hope—it takes a sound financial strategy. Establishing attainable financial objectives is essential to ensuring a solid future. We’ll go over what financial planning includes, how to get started with long-term financial planning, and why it’s critical to realizing your financial goals in this blog.
The Focus of Setting Long-Term Financial Goals
It is always important to identify short-term financial objectives, and mid-term, and long-term when it comes to probabilities to make proper financial securities. If no particular objectives are set, one may turn out to waste money on things that won’t benefit him or her in the long run and may lack money for emergencies or even for their retirement period. This results in a cycle where one first is unable to meet the cost of basic credit card repayments and then resorts to using credit cards to pay for the insurance, which is in most cases expensive, thus creating a field where one is always at the mercy of the major risks of life.

It is always wise to consult and rely on professionals, like the Joseph Stone Capital team, as they may provide tips and advice on how to undertake the measures required for a more secure financial future.
Developing a personalized plan with short- and long-term objectives that are suited to each person’s financial circumstances is known as financial planning. It takes into account preferences, time horizons, past performance, present financial situation, and risk appetite. Planning for the short term takes care of pressing requirements like emergency funds or vacation savings. By establishing clear objectives and making adjustments for shifting conditions, long-term planning seeks to ensure a comfortable future.
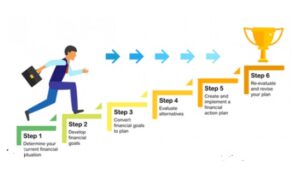
Setting Up Your Financial Goal and Types of Goals
To briefly explain, there are other variables like market fluctuations, inflation rates and so on that can easily influence financial planning of goals. Here is the smart way how you strategize your finances to get lasting results.
• Assess Your Current Financial Status: When developing a budget start, with the gross income, net expenses, the rate of interest, and the amount invested.
• Determine Your Short-Term and Long-Term Objectives: Make a distinction between your tactical demands, like as getting ready for a vacation or purchasing a car, and your strategic plans, which can include building money for future goals like retirement planning.
• Consider Inflation and Market Trends: It is important to consider the inflationary forces as well as market conditions when establishing such targets. Never set goals and objectives that have been rendered irrelevant by changing economic conditions, revise those goals, and make them feasible in the current global economic reality.
• Make a Realistic Budget: Assemble a budget that takes your income, outgoings, and savings into account. Set up money for your objectives while making sure you can pay for everyday expenditures and unexpected crises.
• Invest Diversely: Look into fixed deposit accounts, equities, mutual funds, and real estate. By maximizing returns and minimizing risks, portfolio diversification may hasten the process of reaching your financial objectives.
Conclusion
For financial success, long-term planning helps you achieve your dreams, understand your financial situation, set realistic goals, and ensure stability. While you can manage finances independently, consulting a financial advisor like Joseph Stone Capital is highly recommended. Their expertise ensures your financial planning is comprehensive, covering all critical aspects. A qualified adviser helps you get on the path to a safe financial future by offering insightful advice.
FAQs
Which Common Financial Objectives Are There?
People set various financial goals to achieve stability and security. There are some common examples like clearing debts, setting an early retirement, saving house down payment and even looking after a kid’s future education.
To what extent is budget preparation necessary?
When it comes to financial planning, preparing the budget is important so you know your goals well. It will also help you reach your aims like saving money and clearing debts.